Views: 222 Author: Tina Publish Time: 2025-05-29 Origin: Site









Content Menu
● What is a Backlight LCD Display?
● How Does Backlight Work in LCDs?
● The History and Evolution of LCD Backlighting
>> Early Backlighting Solutions
>> The Rise of CCFL Backlights
● Types of Backlight Technologies
>> CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp) Backlight
>> EL (Electroluminescent) Backlight
● Edge-Lit vs. Direct-Lit LED Backlights
● Advanced Backlight Technologies: Mini-LED and Quantum Dot
● Advantages of LED Backlight LCD Displays
● Applications of Backlight LCD Displays
● Common Issues and Limitations
● The Future of Backlight LCD Technology
>> 1. What is the main difference between LED and CCFL backlights in LCDs?
>> 2. Why can't LCDs display true black?
>> 3. What is local dimming in LED-backlit LCDs?
>> 4. How do edge-lit and direct-lit LED backlights differ?
>> 5. Are backlight LCD displays environmentally friendly?
LCD technology is everywhere—from your smartphone and laptop to TVs, car dashboards, and even wristwatches. But have you ever wondered how these screens produce such vivid images, especially in the dark? The answer lies in a crucial component: the backlight. This comprehensive article explores what a backlight LCD display is, how it works, the different backlighting technologies, their advantages, and much more.

A backlight LCD display is a type of liquid crystal display (LCD) that uses an internal light source—called a backlight—to illuminate the screen from behind or from the sides. Unlike self-emissive displays (such as OLED), LCDs cannot generate their own light. The backlight is essential for making the images visible, especially in low-light or dark environments.
Key Points:
- LCDs require a backlight because liquid crystals do not emit light on their own.
- The backlight is positioned behind or at the edges of the LCD panel.
- Backlighting is used in everything from TVs and monitors to smartphones, watches, and calculators.
The backlighting process in an LCD display involves several critical steps:
1. Light Generation: The backlight source (LEDs or CCFLs) produces light.
2. Diffusion: A diffuser panel spreads the light evenly across the screen.
3. Polarization: The light passes through polarizing filters and the liquid crystal layer.
4. Manipulation: Liquid crystals, controlled by electrical signals, twist to allow varying amounts of light through each pixel.
5. Color Creation: Each pixel is subdivided into red, green, and blue sub-pixels, which combine to create the full spectrum of colors.
This precise control allows LCDs to display sharp, vibrant images with accurate colors.
The journey of LCD backlighting has been marked by significant innovation. The earliest LCDs were reflective and relied solely on ambient light, making them difficult to read in low-light conditions. As demand grew for more versatile and brighter displays, manufacturers began integrating backlights.
Initially, electroluminescent (EL) panels and small incandescent bulbs were used for backlighting, especially in calculators and early digital watches. These solutions were limited in brightness and efficiency.
With the advent of larger LCDs for monitors and televisions, cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs) became the standard. CCFLs provided the necessary brightness and uniformity for larger screens, but they were bulky, consumed more power, and contained hazardous materials like mercury.
The introduction of light-emitting diode (LED) backlights marked a turning point. LEDs are smaller, more energy-efficient, and mercury-free. They enabled thinner displays, better brightness control, and paved the way for advanced features like local dimming and high dynamic range (HDR).
There are several types of backlight technologies used in LCDs, each with its own characteristics:
- Most common in modern LCDs
- Uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as the light source
- Available in two main configurations: edge-lit and direct-lit
- Previously dominant in older LCDs
- Uses fluorescent tubes
- Bulkier and less energy-efficient than LEDs
- Thin, flexible, and low-power
- Used in specialized applications
- Uses fiber optic sheets illuminated by a single light source
- Offers uniform brightness and is ideal for custom shapes
| Feature | Edge-Lit LED Backlight | Direct-Lit (Full Array) LED Backlight |
|---|---|---|
| LED Placement | LEDs along the edges of the panel | LEDs arranged in a grid behind the panel |
| Thickness | Enables ultra-thin designs | Thicker due to more LEDs |
| Brightness | Good, but may have less uniformity | Excellent uniformity and higher peak brightness |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost | Higher cost due to more LEDs |
| Power Usage | More energy-efficient | Consumes more power |
| Local Dimming | Limited or none | Supports advanced local dimming |
| Applications | Slim TVs, monitors, laptops | High-end TVs, professional displays |
Edge-lit backlights are popular for slim devices, while direct-lit backlights are favored for high-end displays that require superior brightness and contrast.
As consumer expectations for display quality rise, manufacturers have developed new backlighting technologies to push the boundaries of LCD performance.
Mini-LED technology uses thousands of tiny LEDs arranged in a dense grid behind the LCD panel. This allows for:
- Finer Local Dimming: More precise control over brightness in small zones, resulting in deeper blacks and less blooming.
- Higher Peak Brightness: Mini-LEDs can achieve much higher brightness levels, ideal for HDR content.
- Improved Uniformity: The dense array of LEDs provides more consistent illumination across the screen.
Mini-LED backlighting is now found in premium TVs, monitors, and tablets, offering performance that rivals some OLED displays while maintaining the advantages of LCDs.
Quantum dots are nanocrystals that emit pure, vibrant colors when illuminated by a light source. When used in combination with LED backlights, quantum dot films can:
- Expand Color Gamut: Achieve more accurate and saturated colors, especially in greens and reds.
- Increase Brightness: Quantum dots are highly efficient, allowing for brighter displays without increasing power consumption.
- Enhance HDR: The improved color and brightness capabilities make quantum dot LCDs ideal for high dynamic range content.
- Long Lifespan: LEDs can last over 50,000 hours, outlasting CCFLs and other technologies.
- Energy Efficiency: Consumes 20–30% less power than CCFL backlights.
- Brightness and Uniformity: Provides excellent brightness and even light distribution.
- Slim Design: Enables ultra-thin screens for modern, sleek devices.
- Color Gamut: Advanced LED backlights (such as RGB-LED or quantum dot) offer a wider range of colors.
- Environmentally Friendly: LEDs do not contain hazardous materials like mercury.
- Instant On/Off: LED backlights reach full brightness instantly, unlike CCFLs, which may require warm-up time.
- Dimming Capabilities: LEDs can be dimmed to very low levels, allowing for adaptive brightness and energy savings.
- Durability: LEDs are solid-state components, making them more resistant to shock and vibration than fragile fluorescent tubes.
Backlight LCD displays are used in a wide variety of devices and industries:
- Consumer Electronics: TVs, smartphones, tablets, laptops, monitors
- Automotive: Dashboard displays, infotainment systems
- Medical Devices: Diagnostic monitors, medical instruments
- Industrial Equipment: Control panels, measurement devices
- Public Displays: Digital signage, advertising boards
- Wearables: Smartwatches, fitness trackers
- Small Electronics: Calculators, clocks, handheld devices
- Aerospace and Defense: Ruggedized LCDs with high-brightness backlights for cockpit displays and field equipment.
- Outdoor Displays: High-luminance backlights for visibility in direct sunlight, used in kiosks, ATMs, and outdoor advertising.
- Gaming Monitors: High refresh rate and HDR support enabled by advanced backlighting for immersive gaming experiences.
While backlight LCD displays offer many benefits, they also have some limitations:
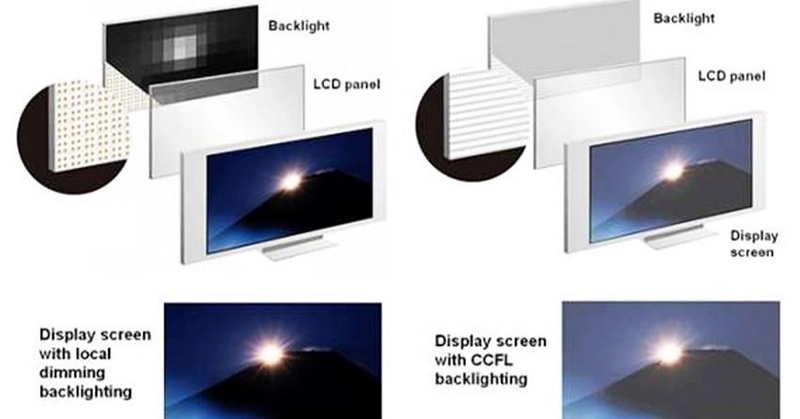
- True Black Levels: LCDs cannot achieve true blacks because the backlight always emits some light, even when pixels are "off."
- Blooming/Halo Effect: Local dimming can cause bright halos around bright objects on dark backgrounds.
- Viewing Angles: Some LCDs may have color and contrast shifts when viewed from the side.
- Power Consumption: While efficient, backlights still consume more power than self-emissive technologies like OLED when displaying dark content.
- Color Shift: In lower-quality panels, colors may appear washed out or shift at extreme angles.
- Backlight Bleed: Uneven light distribution can cause bright spots or patches, especially along the edges of the screen.
The evolution of backlight technology continues to enhance LCD performance:
- Mini-LED: Uses thousands of tiny LEDs for more precise local dimming and higher contrast.
- Micro-LED: Promises even greater efficiency and performance, though still in early stages for mass-market LCDs.
- Quantum Dot Enhancement: Expands color gamut and improves brightness.
- Smart Dimming Algorithms: Advanced control of backlight zones for better HDR (High Dynamic Range) performance.
- Flexible and Transparent Displays: Research is ongoing into flexible and transparent LCDs with innovative backlighting solutions for next-generation devices.
While OLED and Micro-LED displays offer self-emissive pixels that can achieve perfect blacks and infinite contrast, LCDs with advanced backlighting remain more affordable and are available in a wider range of sizes. The ongoing development of backlight technology ensures that LCDs will continue to play a vital role in the display market for years to come.
Backlight LCD displays are a cornerstone of modern digital life, powering screens in nearly every device we use. By using sophisticated backlighting systems—especially LED technology—LCDs achieve bright, sharp, and colorful images in a variety of environments. As technology advances, innovations like mini-LED and quantum dot backlighting continue to push the boundaries of what LCDs can do. Understanding the principles, advantages, and limitations of backlight LCD displays helps users make informed choices when selecting their next device.

LED backlights use light-emitting diodes, which are more energy-efficient, last longer, and allow for thinner screens compared to CCFL (cold cathode fluorescent lamp) backlights, which use fluorescent tubes.
LCDs rely on a backlight that is always on to some extent, so even when pixels are intended to be black, some light leaks through, preventing true black levels.
Local dimming is a feature where the backlight is divided into zones that can be dimmed or brightened independently, improving contrast and black levels in specific areas of the screen.
Edge-lit backlights place LEDs along the edges of the display and use light guides to distribute light, enabling thin designs. Direct-lit backlights position LEDs in a grid behind the screen, offering better uniformity and local dimming capabilities but resulting in a thicker display.
LED backlight LCDs are more environmentally friendly than older technologies because LEDs do not contain hazardous substances like mercury and are more energy-efficient, reducing overall power consumption.
This comprehensive article answers the question "Can I Upgrade My E-Bike LCD Display Easily?" by exploring display types, compatibility, practical upgrade steps, troubleshooting, and maintenance tips. Boost your riding experience and get the most from your LCD display e-bike with the best current advice, illustrations, and video guidance.
This comprehensive guide explores the troubleshooting and repair of backpack LCD display issues, covering blank screens, flickers, garbled text, address conflicts, and more. It offers stepwise solutions and practical videos to help users swiftly restore functionality in their hardware projects.
Discover why the Sharp memory LCD display outperforms traditional LCDs with lower power use, unmatched sunlight readability, robust reliability, and a straightforward interface. Learn about its technology, applications, pros and cons, integration tips, and get answers to common engineering questions.
OLED displays, though admired for their visuals, may cause digital eye strain or "OLED screen eye tire" during extended use because of blue light, potential PWM flicker, and intense color/contrast. By using optimal settings and healthy habits, users can safely enjoy OLED with minimal discomfort.
Does displaying a white screen on an LG OLED TV fix persistent burn-in? The answer is no: true burn-in results from irreversible pixel wear and chemical aging. The best practice is to use preventive features, moderate settings, and varied content to safeguard screen health. For severe cases, panel replacement is the only cure.
An in-depth guide to the LCD display bezel: its definition, history, materials, structure, and growing role in display design. Explores bezel importance, types, aesthetic trends, maintenance, and innovation, offering expert insights—including an expanded FAQ and practical visuals—to help users understand its unique place in technology.
This article provides a complete, practical guide to diagnosing and fixing non-responsive SPI LCD displays using methods including hardware validation, logic level correction, library configuration, and advanced diagnostic tools. Perfect for hobbyists and engineers alike.
LCD display liquid coolers deliver top-tier performance with visually stunning customizable LCD panels that display system data and artwork. They suit enthusiasts and streamers aiming for unique builds but may be unnecessary for budget or basic systems. The price premium is justified by advanced hardware, software, and customization features.
Black bars on an OLED screen do not cause burn-in as those pixels are switched off. Only with excessive, repetitive content does minor uneven aging become possible. Varying viewing habits and enabling panel maintenance prevents problems in daily use.
OLED TVs provide spectacular picture quality but rely heavily on the quality of the video input. Most cable broadcasts are limited to lower resolutions and compressed formats, so an OLED screen connected to a regular cable box will look better than older TVs but may not realize its full potential. Upgrading cable boxes and utilizing streaming services can unlock the best OLED experience.
OLED screen burn-in remains one of the key challenges inherent in this display technology. While no universal fix exists for permanent burn-in, a blend of app-based tools, manufacturer features, and maintenance practices can help reduce appearance and delay onset. Proper prevention strategies and use of built-in pixel shift and refresher tools offer the best chances of avoiding this issue.
This article comprehensively explores will OLED screen burn in over time by explaining the science of OLED displays, causes and types of burn in, manufacturer solutions, prevention tips, and real-world user experiences. Burn in risk does exist, but modern panels and user habits greatly reduce its likelihood, making OLED an excellent and long-lasting display choice.
This article provides an in-depth guide to selecting the best LCD display driver IC for various applications, covering driver types, key features, leading manufacturers, integration tips, and practical examples. It includes diagrams and videos to help engineers and hobbyists make informed decisions about LCD display driver selection.
Dead pixels are a common type of LCD display defect, caused by manufacturing faults, physical damage, or environmental factors. While stuck pixels may be fixable, dead pixels are usually permanent. Proper care and understanding can help prevent and address these issues.
This comprehensive guide explains every symbol and function found on e-bike LCD displays, using clear explanations and practical tips. Learn to interpret battery, speed, PAS, error codes, and customize settings using your e-bike LCD display manual for a safer, smarter ride.
This comprehensive guide explains how to set an LCD display clock, covering everything from hardware setup and wiring to coding, troubleshooting, and creative customization. With detailed instructions and practical tips, you'll learn to confidently build and personalize your own LCD display clock for any setting.
This article explores whether OLED laptop screens are prone to burn-in, examining the science, real-world evidence, prevention methods, and lifespan. It provides practical advice and answers common questions to help users make informed decisions about OLED technology.
Displaying a black screen on an OLED TV will not cause burn-in, as the pixels are turned off and not subject to wear. Burn-in is caused by static, bright images over time. With proper care and built-in features, OLED TVs are reliable and offer exceptional picture quality.
This article explores the causes of OLED screen burn-in, the science behind it, and effective prevention strategies. It covers signs, effects, and potential fixes, with practical tips to prolong your OLED display's lifespan and answers to common questions about burn-in.
OLED screens deliver unmatched image quality, with perfect blacks, vivid colors, and ultra-fast response times. Despite higher costs and some risk of burn-in, their advantages make them the top choice for premium displays in TVs, smartphones, and monitors.