Views: 222 Author: Tina Publish Time: 2025-01-19 Origin: Site









Content Menu
● Understanding the I2C 16x2 LCD Display
● Wiring the I2C 16x2 LCD Display
● Installing Necessary Libraries
● Advanced Features of I2C LCDs
● Applications of I2C LCDs in Projects
● FAQ
>> 2: How do I find my I2C address?
>> 3: Can I use this LCD with any Arduino model?
>> 4: How do I clear the display?
>> 5: What should I do if nothing displays?
Connecting an I2C 16x2 LCD display to an Arduino is a straightforward process that simplifies the wiring and coding required compared to traditional LCD setups. This guide will provide detailed instructions on how to connect, code, and utilize an I2C LCD display with your Arduino projects.

The I2C 16x2 LCD is a type of liquid crystal display that can show up to 16 characters per line on two lines. The "I2C" (Inter-Integrated Circuit) interface allows for communication using only two wires, significantly reducing the number of connections needed compared to parallel interfaces.
- 16 Characters per Line: Displays a total of 32 characters.
- Two Lines: Allows for multi-line text display.
- I2C Interface: Uses only four pins (VCC, GND, SDA, SCL) for connection.
- Backlight: Most models come with a backlight for better visibility.
To get started, you will need the following components:
- Arduino Board (e.g., Arduino Uno)
- 16x2 I2C LCD Display
- I2C Module (often included with the LCD)
- Jumper Wires (4 male-to-female jumper wires)
- Breadboard (optional, for easier connections)

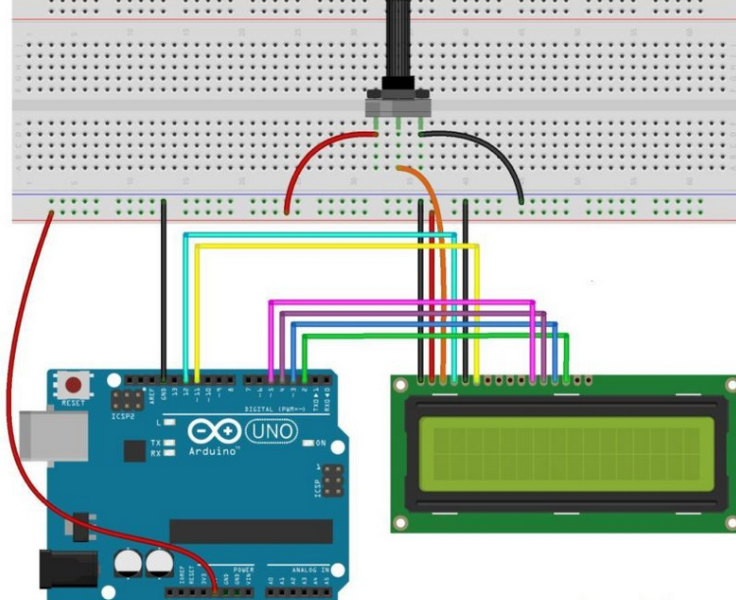
The wiring process is simple. Below are the connections you need to make:
1. Connect the Power Pins:
- Connect the VCC pin on the I2C module to the 5V pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the GND pin on the I2C module to the GND pin on the Arduino.
2. Connect the Data Pins:
- Connect the SDA pin on the I2C module to A4 on the Arduino (SDA).
- Connect the SCL pin on the I2C module to A5 on the Arduino (SCL).
Before you can use your I2C LCD display, you need to install a library that facilitates communication between your Arduino and the display.
1. Open the Arduino IDE.
2. Navigate to `Sketch` > `Include Library` > `Manage Libraries`.
3. In the Library Manager, search for "LiquidCrystal_I2C" and install it.
1. Connect your Arduino to your computer via USB.
2. Select the correct board and port in your Arduino IDE.
3. Upload your code.
4. You should see "Hello World!" displayed on your LCD followed by "Arduino & I2C".

If your display does not show anything or behaves unexpectedly:
- Ensure all connections are secure.
- Check that you are using the correct I2C address in your code.
- Adjust the contrast potentiometer on the back of some displays if available.
- Verify that you have installed all necessary libraries correctly.
Beyond basic text display functionality, I2C LCDs offer several advanced features that can enhance user interaction and experience in projects:
You can create custom characters or icons using a specific function provided by libraries like LiquidCrystal_I2C. This allows you to represent unique symbols or graphics that can be displayed alongside standard text.
For longer messages that exceed one line of display capacity, you can implement scrolling text features that will allow messages to move across the screen smoothly.
If you have several I2C displays, it's possible to connect them all using different addresses and control them from a single Arduino board. This can be particularly useful in larger projects where multiple outputs are needed.
The versatility of I2C LCDs makes them suitable for various applications:
- Data Monitoring: Display sensor data such as temperature or humidity readings in real-time.
- User Interfaces: Create interactive user interfaces for projects like robots or home automation systems where user feedback is essential.
- Educational Projects: Ideal for learning environments where students can visualize data from experiments or programming exercises.
Connecting an I2C 16x2 LCD display to an Arduino is a simple yet effective way to enhance your projects with visual output capabilities. By following this guide, you can easily wire up your display, install necessary libraries, find its address, and write basic code to control it.
An I2C LCD is a liquid crystal display that uses an inter-integrated circuit protocol for communication, allowing multiple devices to connect using only two wires.
You can find your I2C address by using an I2C scanner sketch that checks all possible addresses and reports any devices it finds.
Yes, as long as you connect it correctly according to each model's specific SDA and SCL pins.
You can clear the display using `lcd.clear()` in your code.
Check all connections, ensure you're using the correct I2C address in your code, and adjust any contrast settings if available.
[1] https://deepbluembedded.com/arduino-i2c-lcd/
[2] https://arduinointro.com/articles/projects/simple-led-meter-using-potentiometer-and-i2c-lcd
[3] https://forum.arduino.cc/t/i2c-lcd-16x2-not-working/1175746
[4] https://www.instructables.com/LCD-With-I2C/
[5] https://randomnerdtutorials.com/esp32-esp8266-i2c-lcd-arduino-ide/
[6] https://forum.arduino.cc/t/i2c-lcd-display-not-working/1066696
[7] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RZOqqbT_r3k
[8] https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/how-to-interface-i2c-lcd-display-with-arduino/
[9] https://forum.arduino.cc/t/i2c-lcd-doesnt-display-text-solved/600002
[10] https://lastminuteengineers.com/i2c-lcd-arduino-tutorial/
[11] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CvqHkXeXN3M
[12] https://forum.arduino.cc/t/i2c-lcd-not-displaying/1033760
[13] https://www.instructables.com/How-to-Connect-I2C-Lcd-Display-to-Arduino-Uno/
[14] https://forum.arduino.cc/t/problem-with-i2c-lcd-display/650358
[15] https://arduinogetstarted.com/tutorials/arduino-lcd-i2c
[16] https://forum.arduino.cc/t/i2c-lcd-does-not-work-solved/630985
[17] https://arduino.stackexchange.com/questions/93735/lcd-i2c-connection-problems
[18] https://electronoobs.com/eng_arduino_tut51.php
[19] https://forum.arduino.cc/t/troubleshooting-16x2-lcd-display-with-i2c-interface/280867
This comprehensive article answers the question "Can I Upgrade My E-Bike LCD Display Easily?" by exploring display types, compatibility, practical upgrade steps, troubleshooting, and maintenance tips. Boost your riding experience and get the most from your LCD display e-bike with the best current advice, illustrations, and video guidance.
This comprehensive guide explores the troubleshooting and repair of backpack LCD display issues, covering blank screens, flickers, garbled text, address conflicts, and more. It offers stepwise solutions and practical videos to help users swiftly restore functionality in their hardware projects.
Discover why the Sharp memory LCD display outperforms traditional LCDs with lower power use, unmatched sunlight readability, robust reliability, and a straightforward interface. Learn about its technology, applications, pros and cons, integration tips, and get answers to common engineering questions.
OLED displays, though admired for their visuals, may cause digital eye strain or "OLED screen eye tire" during extended use because of blue light, potential PWM flicker, and intense color/contrast. By using optimal settings and healthy habits, users can safely enjoy OLED with minimal discomfort.
Does displaying a white screen on an LG OLED TV fix persistent burn-in? The answer is no: true burn-in results from irreversible pixel wear and chemical aging. The best practice is to use preventive features, moderate settings, and varied content to safeguard screen health. For severe cases, panel replacement is the only cure.
An in-depth guide to the LCD display bezel: its definition, history, materials, structure, and growing role in display design. Explores bezel importance, types, aesthetic trends, maintenance, and innovation, offering expert insights—including an expanded FAQ and practical visuals—to help users understand its unique place in technology.
This article provides a complete, practical guide to diagnosing and fixing non-responsive SPI LCD displays using methods including hardware validation, logic level correction, library configuration, and advanced diagnostic tools. Perfect for hobbyists and engineers alike.
LCD display liquid coolers deliver top-tier performance with visually stunning customizable LCD panels that display system data and artwork. They suit enthusiasts and streamers aiming for unique builds but may be unnecessary for budget or basic systems. The price premium is justified by advanced hardware, software, and customization features.
Black bars on an OLED screen do not cause burn-in as those pixels are switched off. Only with excessive, repetitive content does minor uneven aging become possible. Varying viewing habits and enabling panel maintenance prevents problems in daily use.
OLED TVs provide spectacular picture quality but rely heavily on the quality of the video input. Most cable broadcasts are limited to lower resolutions and compressed formats, so an OLED screen connected to a regular cable box will look better than older TVs but may not realize its full potential. Upgrading cable boxes and utilizing streaming services can unlock the best OLED experience.
OLED screen burn-in remains one of the key challenges inherent in this display technology. While no universal fix exists for permanent burn-in, a blend of app-based tools, manufacturer features, and maintenance practices can help reduce appearance and delay onset. Proper prevention strategies and use of built-in pixel shift and refresher tools offer the best chances of avoiding this issue.
This article comprehensively explores will OLED screen burn in over time by explaining the science of OLED displays, causes and types of burn in, manufacturer solutions, prevention tips, and real-world user experiences. Burn in risk does exist, but modern panels and user habits greatly reduce its likelihood, making OLED an excellent and long-lasting display choice.
This article provides an in-depth guide to selecting the best LCD display driver IC for various applications, covering driver types, key features, leading manufacturers, integration tips, and practical examples. It includes diagrams and videos to help engineers and hobbyists make informed decisions about LCD display driver selection.
Dead pixels are a common type of LCD display defect, caused by manufacturing faults, physical damage, or environmental factors. While stuck pixels may be fixable, dead pixels are usually permanent. Proper care and understanding can help prevent and address these issues.
This comprehensive guide explains every symbol and function found on e-bike LCD displays, using clear explanations and practical tips. Learn to interpret battery, speed, PAS, error codes, and customize settings using your e-bike LCD display manual for a safer, smarter ride.
This comprehensive guide explains how to set an LCD display clock, covering everything from hardware setup and wiring to coding, troubleshooting, and creative customization. With detailed instructions and practical tips, you'll learn to confidently build and personalize your own LCD display clock for any setting.
This article explores whether OLED laptop screens are prone to burn-in, examining the science, real-world evidence, prevention methods, and lifespan. It provides practical advice and answers common questions to help users make informed decisions about OLED technology.
Displaying a black screen on an OLED TV will not cause burn-in, as the pixels are turned off and not subject to wear. Burn-in is caused by static, bright images over time. With proper care and built-in features, OLED TVs are reliable and offer exceptional picture quality.
This article explores the causes of OLED screen burn-in, the science behind it, and effective prevention strategies. It covers signs, effects, and potential fixes, with practical tips to prolong your OLED display's lifespan and answers to common questions about burn-in.
OLED screens deliver unmatched image quality, with perfect blacks, vivid colors, and ultra-fast response times. Despite higher costs and some risk of burn-in, their advantages make them the top choice for premium displays in TVs, smartphones, and monitors.