Views: 222 Author: Tina Publish Time: 2025-03-20 Origin: Site








Content Menu
● Introduction to LCD Displays and Arduino
>> Understanding LCD Communication Protocols
>> TFT Displays
● FAQ
>> 1. How do I connect an LCD display to Arduino?
>> 2. What is the purpose of pulldown resistors?
>> 3. How do I handle fast data rates?
>> 4. Why am I reading invalid characters?
>> 5. Can I use other types of LCDs with Arduino?
>> 6. How Do I Connect an LCD Display to Arduino?
>> 7. What Is the Purpose of Pulldown Resistors?
>> 8. How Do I Handle Fast Data Rates?
>> 9. Why Am I Reading Invalid Characters?
>> 10. Can I Use Other Types of LCDs with Arduino?
Extracting data from LCD displays using Arduino involves several steps, including understanding the LCD's communication protocol, setting up the hardware, and implementing the necessary software to read and interpret the data. This article will guide you through the process, highlighting key concepts, challenges, and solutions.

LCD displays are widely used in electronic devices for displaying information. They can be controlled by various microcontrollers, including Arduino boards. Arduino is a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals alike due to its ease of use and versatility.
LCD displays typically use protocols like HD44780 for character displays or SPI/I2C for more complex displays. Understanding these protocols is crucial for extracting data.
HD44780 Protocol:
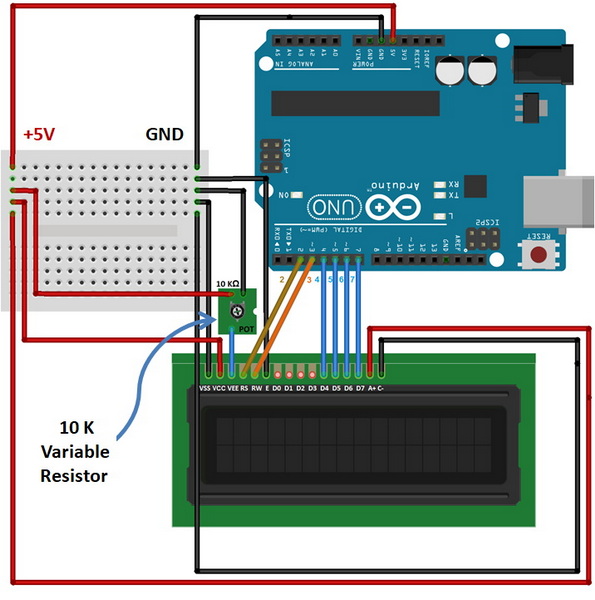
This protocol is commonly used in character LCDs like the LCD1602. It involves control pins (RS, RW, E) and data pins (D0-D7). The RS pin selects whether data is a command or character, RW determines if the LCD is in read or write mode, and E is the enable pin.
SPI/I2C Protocols:
These protocols are used in more advanced displays like TFT LCDs. SPI is faster but requires more pins, while I2C is simpler but slower. SPI typically uses four pins: SCK (clock), MOSI (master out slave in), MISO (master in slave out), and CS (chip select). I2C uses two pins: SCL (clock) and SDA (data).

To extract data from an LCD display using Arduino, you need to connect the display's data bus to the Arduino's digital pins. For character LCDs, this typically involves connecting D0-D7 to digital pins, and RS, RW, E to other digital pins.
Here's a simplified connection diagram for a character LCD:
- D0-D7: Connect these to digital pins on the Arduino (e.g., D0-D7).
- RS: Connect to a digital pin (e.g., Pin 6).
- RW: Connect to a digital pin (e.g., Pin 7).
- E: Connect to a digital pin (e.g., Pin 5).
To avoid reading errors, use pulldown resistors (1kΩ) on each data pin. This ensures that when the LCD is not driving a pin, it reads as low, preventing incorrect readings.
Using a breadboard can simplify the connection process. Place the LCD and Arduino on the breadboard and connect the wires accordingly. Ensure that all connections are secure to prevent loose connections.
The software part involves writing a program to read the data from the LCD's data bus and interpret it.
For faster data reading, use Arduino's port registers instead of `digitalRead()`. This method allows simultaneous reading of multiple pins, which is essential for capturing data from the LCD quickly.
For displays like the LCD1602, you can use protocol sniffers to capture and interpret the data being sent to the display. This involves monitoring the communication between the microcontroller and the LCD to understand the commands and data being transmitted.
Once you capture the data, you need to interpret it according to the LCD's protocol. For character LCDs, this involves recognizing commands like clearing the display or moving the cursor, and data like characters being displayed.
If you're reading invalid characters, ensure that your timing is correct and that you're handling the data bits properly. Incorrect timing can lead to misinterpretation of the data.
The data rate might be too fast for real-time serial printing. Use a queue to consolidate data before printing. This ensures that no data is lost during transmission and that the serial output is coherent.
Electrical noise can interfere with data transmission. Use shielding or keep the setup away from sources of interference to minimize errors.

For more complex displays like TFT LCDs, you'll need to use libraries specific to those displays. These libraries handle the low-level communication, making it easier to display graphics and text.
TFT displays offer higher resolution and color capabilities compared to character LCDs. They are ideal for projects requiring graphical interfaces. However, they require more processing power and memory.
OLED displays are known for their high contrast and low power consumption. They are suitable for battery-powered devices and offer a sleeker appearance.
Extracting data from LCD displays can be useful in various applications:
- Reverse Engineering: Understanding how an LCD display communicates can help in reverse-engineering existing devices.
- Automation: By reading data from an LCD, you can automate tasks based on the displayed information.
- Monitoring Systems: In industrial settings, extracting data from LCD displays can be used to monitor system status or parameters.
In industrial environments, LCD displays are often used to show critical system parameters. Extracting this data allows for real-time monitoring and control, enhancing efficiency and safety.
In home automation projects, reading data from LCD displays can help integrate different systems. For example, you can automate lighting or heating based on the data displayed on an LCD screen.
As technology advances, LCD displays are becoming more sophisticated. Future developments may include higher resolution displays and more efficient communication protocols, which will require updated methods for data extraction.
High-resolution displays like those found in smartphones can be challenging to interface with Arduino due to their complex protocols. However, with the right libraries and hardware, it's possible to integrate these displays into Arduino projects.
Integrating wireless communication protocols like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi into LCD display projects allows for remote monitoring and control. This can be particularly useful in IoT applications.
Extracting data from LCD displays using Arduino requires understanding the display's communication protocol, setting up the hardware correctly, and implementing the right software to read and interpret the data. Common challenges include handling fast data rates and ensuring correct timing. With the right approach, you can successfully read data from LCD displays and integrate them into your Arduino projects.

Connect data pins (D0-D7) and control pins (RS, RW, E) to Arduino's digital pins.
They prevent floating inputs on Arduino pins.
Use a buffer or queue to store incoming data.
Check timing and data bit interpretation.
Yes, use SPI or I2C protocols for TFT displays.
To connect an LCD display to Arduino, ensure you have the correct pins connected. For character LCDs, connect data pins (D0-D7) and control pins (RS, RW, E) to Arduino's digital pins. Use a breadboard for easier connections.
Pulldown resistors are used to prevent floating inputs on the Arduino pins. They ensure that when the LCD is not driving a pin, it reads as low, preventing incorrect readings.
For fast data rates, use a buffer or queue to store incoming data before processing or printing it. This ensures that no data is lost during transmission.
Invalid characters often result from incorrect timing or misinterpretation of the data bits. Ensure that your code correctly handles the data protocol and timing of the LCD.
Yes, you can use other types of LCDs like TFT displays with Arduino. These typically use SPI or I2C protocols and require different libraries and connection setups.
This comprehensive article answers the question "Can I Upgrade My E-Bike LCD Display Easily?" by exploring display types, compatibility, practical upgrade steps, troubleshooting, and maintenance tips. Boost your riding experience and get the most from your LCD display e-bike with the best current advice, illustrations, and video guidance.
This comprehensive guide explores the troubleshooting and repair of backpack LCD display issues, covering blank screens, flickers, garbled text, address conflicts, and more. It offers stepwise solutions and practical videos to help users swiftly restore functionality in their hardware projects.
Discover why the Sharp memory LCD display outperforms traditional LCDs with lower power use, unmatched sunlight readability, robust reliability, and a straightforward interface. Learn about its technology, applications, pros and cons, integration tips, and get answers to common engineering questions.
OLED displays, though admired for their visuals, may cause digital eye strain or "OLED screen eye tire" during extended use because of blue light, potential PWM flicker, and intense color/contrast. By using optimal settings and healthy habits, users can safely enjoy OLED with minimal discomfort.
Does displaying a white screen on an LG OLED TV fix persistent burn-in? The answer is no: true burn-in results from irreversible pixel wear and chemical aging. The best practice is to use preventive features, moderate settings, and varied content to safeguard screen health. For severe cases, panel replacement is the only cure.
An in-depth guide to the LCD display bezel: its definition, history, materials, structure, and growing role in display design. Explores bezel importance, types, aesthetic trends, maintenance, and innovation, offering expert insights—including an expanded FAQ and practical visuals—to help users understand its unique place in technology.
This article provides a complete, practical guide to diagnosing and fixing non-responsive SPI LCD displays using methods including hardware validation, logic level correction, library configuration, and advanced diagnostic tools. Perfect for hobbyists and engineers alike.
LCD display liquid coolers deliver top-tier performance with visually stunning customizable LCD panels that display system data and artwork. They suit enthusiasts and streamers aiming for unique builds but may be unnecessary for budget or basic systems. The price premium is justified by advanced hardware, software, and customization features.
Black bars on an OLED screen do not cause burn-in as those pixels are switched off. Only with excessive, repetitive content does minor uneven aging become possible. Varying viewing habits and enabling panel maintenance prevents problems in daily use.
OLED TVs provide spectacular picture quality but rely heavily on the quality of the video input. Most cable broadcasts are limited to lower resolutions and compressed formats, so an OLED screen connected to a regular cable box will look better than older TVs but may not realize its full potential. Upgrading cable boxes and utilizing streaming services can unlock the best OLED experience.
OLED screen burn-in remains one of the key challenges inherent in this display technology. While no universal fix exists for permanent burn-in, a blend of app-based tools, manufacturer features, and maintenance practices can help reduce appearance and delay onset. Proper prevention strategies and use of built-in pixel shift and refresher tools offer the best chances of avoiding this issue.
This article comprehensively explores will OLED screen burn in over time by explaining the science of OLED displays, causes and types of burn in, manufacturer solutions, prevention tips, and real-world user experiences. Burn in risk does exist, but modern panels and user habits greatly reduce its likelihood, making OLED an excellent and long-lasting display choice.
This article provides an in-depth guide to selecting the best LCD display driver IC for various applications, covering driver types, key features, leading manufacturers, integration tips, and practical examples. It includes diagrams and videos to help engineers and hobbyists make informed decisions about LCD display driver selection.
Dead pixels are a common type of LCD display defect, caused by manufacturing faults, physical damage, or environmental factors. While stuck pixels may be fixable, dead pixels are usually permanent. Proper care and understanding can help prevent and address these issues.
This comprehensive guide explains every symbol and function found on e-bike LCD displays, using clear explanations and practical tips. Learn to interpret battery, speed, PAS, error codes, and customize settings using your e-bike LCD display manual for a safer, smarter ride.
This comprehensive guide explains how to set an LCD display clock, covering everything from hardware setup and wiring to coding, troubleshooting, and creative customization. With detailed instructions and practical tips, you'll learn to confidently build and personalize your own LCD display clock for any setting.
This article explores whether OLED laptop screens are prone to burn-in, examining the science, real-world evidence, prevention methods, and lifespan. It provides practical advice and answers common questions to help users make informed decisions about OLED technology.
Displaying a black screen on an OLED TV will not cause burn-in, as the pixels are turned off and not subject to wear. Burn-in is caused by static, bright images over time. With proper care and built-in features, OLED TVs are reliable and offer exceptional picture quality.
This article explores the causes of OLED screen burn-in, the science behind it, and effective prevention strategies. It covers signs, effects, and potential fixes, with practical tips to prolong your OLED display's lifespan and answers to common questions about burn-in.
OLED screens deliver unmatched image quality, with perfect blacks, vivid colors, and ultra-fast response times. Despite higher costs and some risk of burn-in, their advantages make them the top choice for premium displays in TVs, smartphones, and monitors.